|
Primitives |
Arguments |
Use |
|
wait |
n: whole number |
Halts the program, and therefore the turtle, for
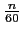 seconds. seconds. |
|
chrono, chronometre |
n: integer |
Starts a countdown of n seconds. We know if this countdown has finished with the primitive endcountdown? |
|
endcountdown? |
none |
Returns "true if there's no active countdown. Returns "false if the countdown is active. |
|
date |
none |
Returns a list wich contains three integers representing the date. The first integer indicates the day, the second the month and the last the year. --> [day month year] |
|
time |
aucun |
Returns a list of three integers representing the time. The first integer indicates the hour, the second the minutes and the last the seconds. --> [hour minute seconde] |
|
pasttime |
none |
Returns the past time in seconds since XLOGO has started. |